Improved Motor Function for Patients with CIDP1
The ProCID study was a prospective, double-blind, randomized, multicenter Phase 3 study that evaluated the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of PANZYGA in adult patients with CIDP.
Key Inclusion Criteria
- Adult patients with CIDP treated with IVIg or corticosteroids
- Weakness of ≥2 limbs
- Adjusted INCAT disability score between 2 and 9a
Study Endpoints
Primary Endpoint
Adjusted INCAT responder rate for the PANZYGA 1 g/kg treatment arm at 6 months relative to baseline
Supporting Efficacy Endpoints
- Adjusted INCAT responder rate for the PANZYGA 2 g/kg treatment arm at 6 months relative to baseline
- For both the 1 g/kg and 2 g/kg treatment arms:
- The time to INCAT response
- I-RODS, Grip Strength, and MRC Sum Score responder rates
Wash-Out Phase
During the wash-out phase, patients had their current medications reduced in a predefined standard manner, to determine whether they had active CIDP. Those with deterioration of CIDP were eligible for the dose-evaluation phase.3
≤12 weeks (IVIg/corticosteroids)
Deterioration of CIDP: decrease in PGIC score and ≥1 of the following:
- Increase in INCAT disability score of ≥1
- Decrease in grip strength of ≥8 kPa in one hand
- I-RODS MCID-SE (cutoff of -1.96 or less)
Dose-Evaluation 1 Phase
(Infusions Every 3 Weeks)c,d
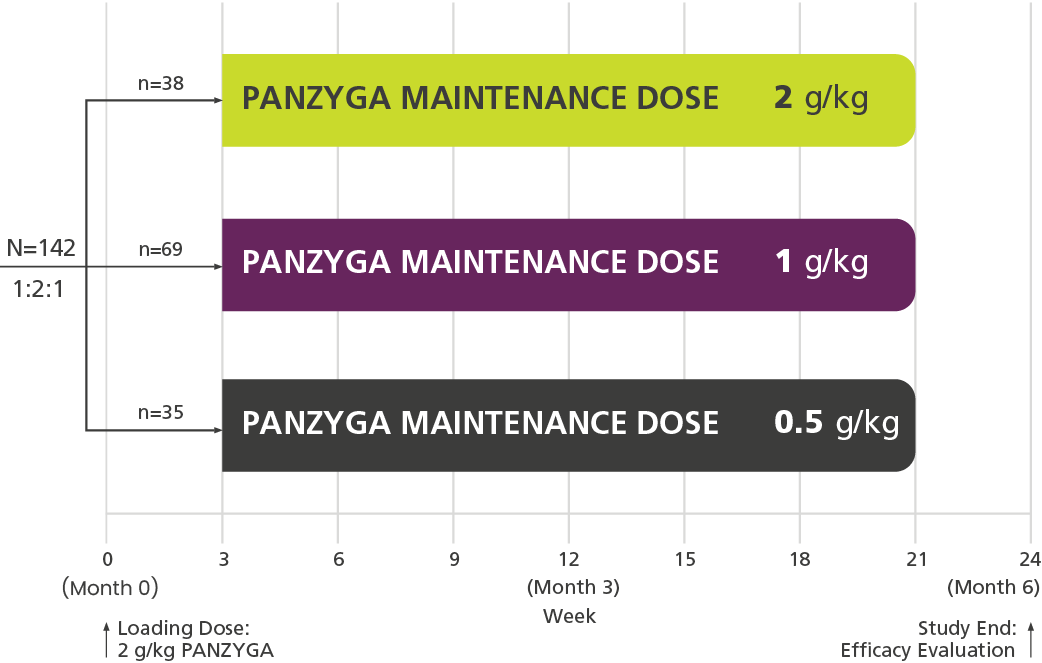
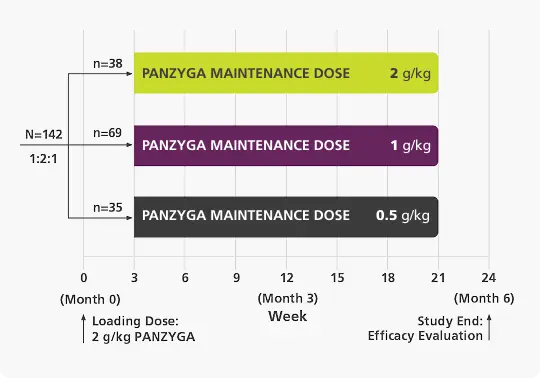
Primary Endpoint
80%
of patients receiving a 1 g/kg PANZYGA maintenance dose achieved an INCAT response at 6 months.
92%
of patients receiving a 2 g/kg PANZYGA maintenance dose achieved an INCAT response at 6 months.
INCAT Responder Rates1, a
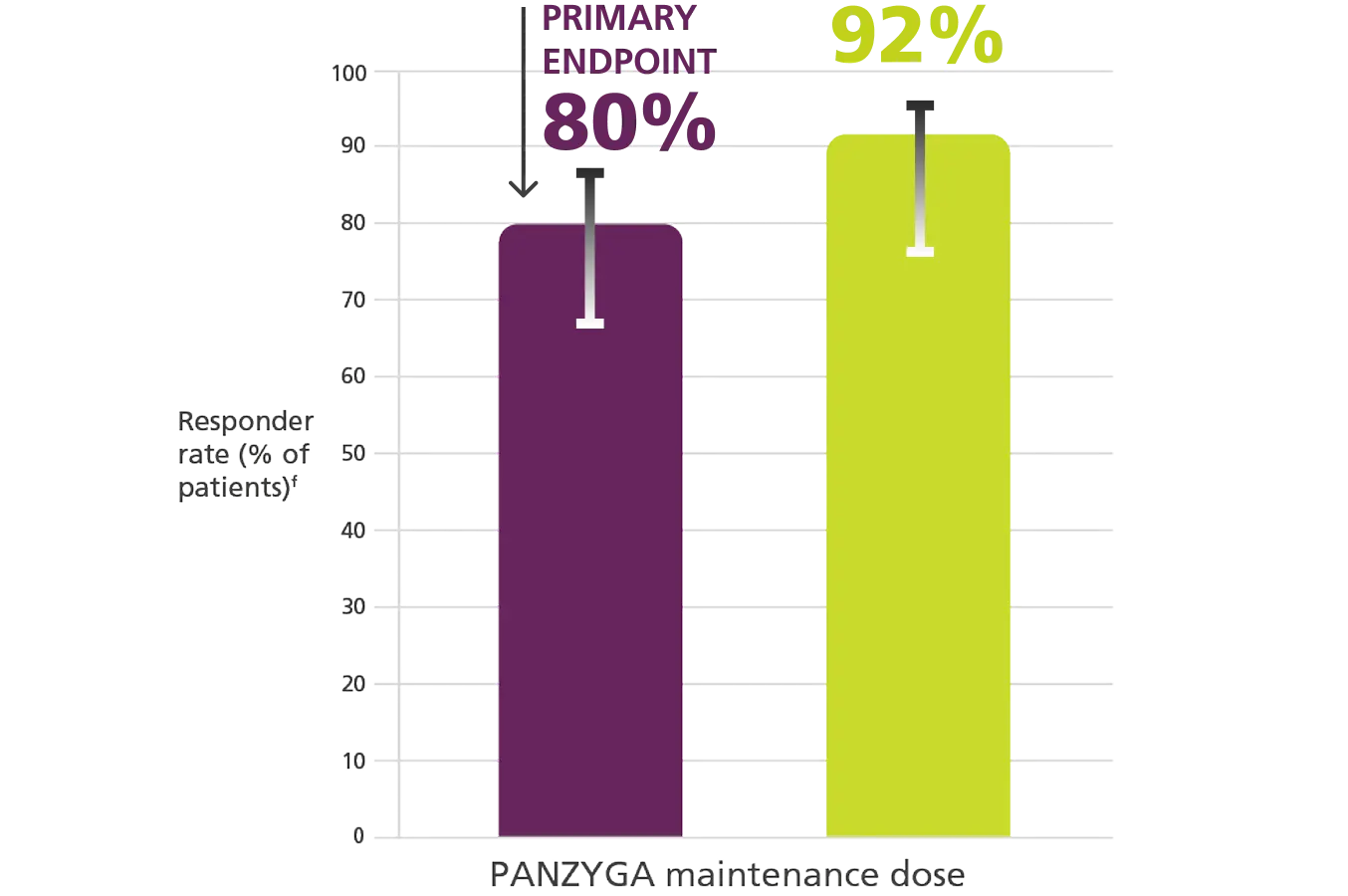
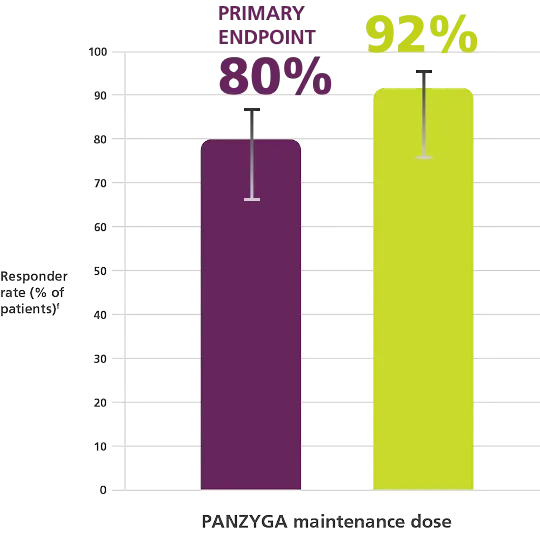
Primary Endpoint
Supporting Efficacy Endpoints1
The median time to first response based on adjusted INCAT score was2:
26 days
for the 1 g/kg arm
23 days
for the 2 g/kg arm
Supporting Efficacy Endpoints:
I-RODS, Grip Strength, and MRC Sum Score Responder
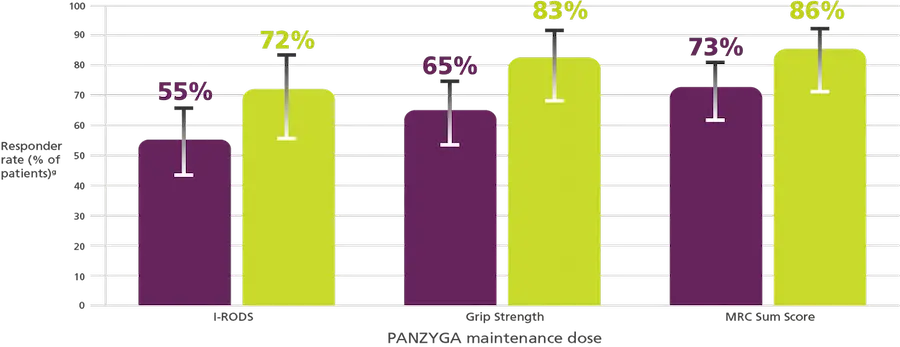
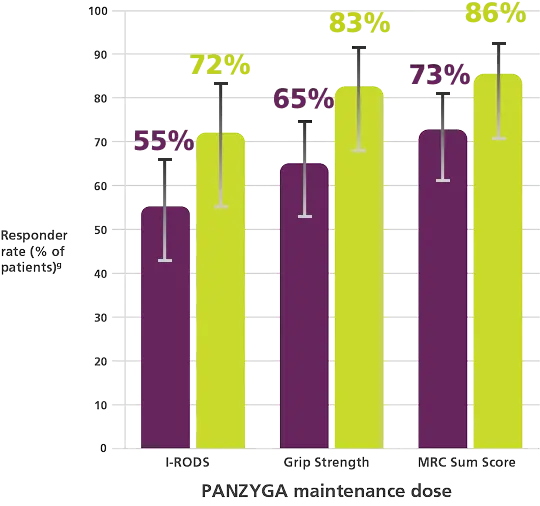
A dose dependent improvement in responder rates was observed for I-RODS, Grip Strength, and MRC Sum Score.
Rescue Dosing
With an approved 2 g/kg maintenance dose option, PANZYGA dosing can be adjusted if clinically needed.1
Rescue Dosing Treatment1,2
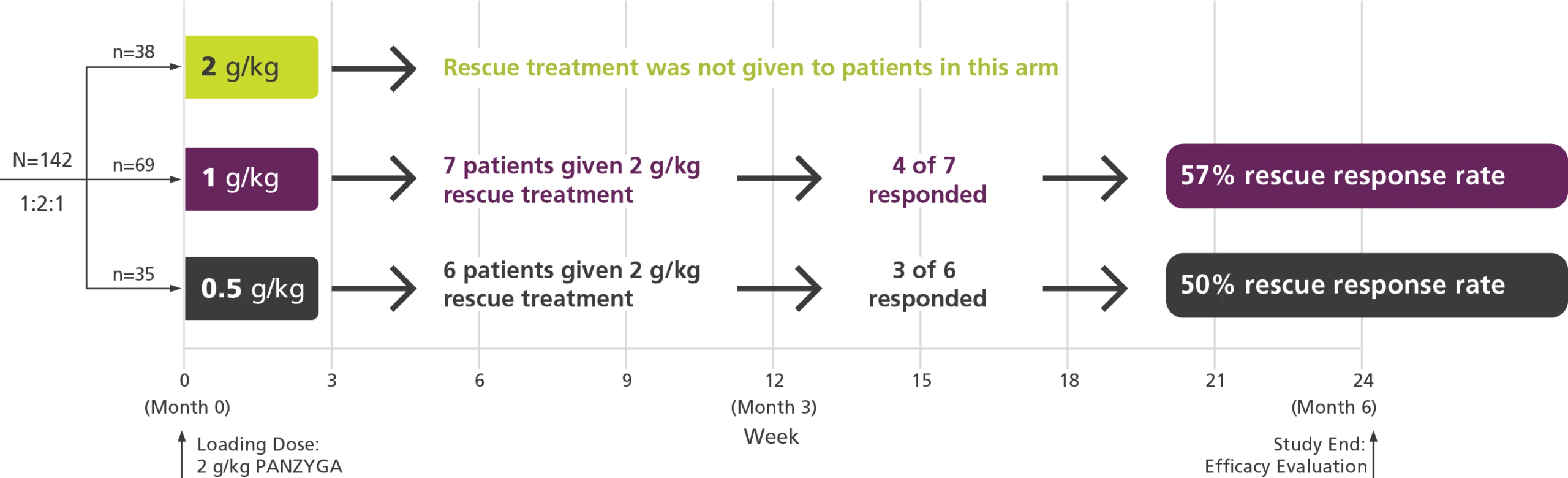
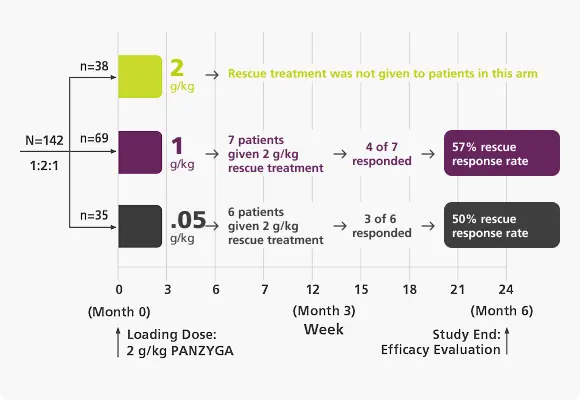
- More than half of patients receiving rescue dosing treatment demonstrated an INCAT response when the dose was increased to 2 g/kg.
- Patients in the 0.5 g/kg and 1 g/kg arms had the option of rescue dosing treatment with 2 consecutive infusions of 2 g/kg at 3 week intervals if clinical criteria were met.

The first and only IVIg treatment study
to evaluate different maintenance
dosing options for CIDP in adults1
CIDP Safety & Tolerability
CIDP = chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy;
INCAT = inflammatory neuropathy cause and treatment;
I-RODS = inflammatory Rasch-built overall disability scale;
IVIg = intravenous immunoglobulin;
MCID-SE = minimal clinical importance difference standard errors;
MRC = Medical Research Council;
PGIC = patient global impression of change.
aAn INCAT Score of 2 comes exclusively from leg disability.2
bResponders were defined as patients with a decrease of at least 1 point on the adjusted INCAT disability score relative to baseline.
cIf patients in the 0.5 g/kg or 1 g/kg arms were either deteriorating at a 3-week interval after Week 3 and before Week 18 or not improving at Week 6,
they were given 2 consecutive blinded doses of 2 g/kg 3 weeks apart. Their improvement was assessed with a study-end visit 3 weeks after the second
rescue dose, and then they were discontinued. Patients in the 2 g/kg arm who were either deteriorating at a 3-week interval after Week 3 and before
Week 18 or not improving at Week 6 were discontinued.2
dSince previous placebo-controlled studies have already been done, it was not considered ethically justified to conduct further placebo-controlled studies.2
eResponders are defined as patients with a decrease of at least 1 point in INCAT score relative to baseline.
fResponder rates were 79.7% (55 of 69 patients) in the 1 g/kg arm (95% CI, 69%-88%) and 91.7% (33 of 36 patients) in the 2 g/kg arm
(95% CI, 78%-97%).1
gResponders defined as the following:
- I-RODS = Scores using minimum clinically important difference related to the varying standard errors (MCID-SE). Responder rates were 55.1%
(38 of 69 patients) in the 1 g/kg arm (95% CI, 43%-66%) and 72.2% (26 of 36 patients) in the 2 g/kg arm (95% CI, 56%-84%). - Grip Strength = Minimum clinically important difference (MCID) cutoff of 8 kPa. Responder rates were 65.2% (45 of 69 patients) in the 1 g/kg arm
(95% CI, 53%-75%) and 83.3% (30 of 36 patients) in the 2 g/kg arm (95% CI, 68%-92%). - MRC Sum Score = Increase of at least 4 points compared with baseline. Responder rates were 72.5% (50 of 69 patients) in the 1 g/kg group
(95% CI, 61%-82%) and 86.1% (31 of 36 patients) in the 2 g/kg arm (95% CI, 71%-94%).1,2
References: 1. Panzyga. Prescribing information. Octapharma USA, Inc.; 2021. 2. Data on file. Octapharma USA, Inc. 3. Cornblath DR, van Doorn PA, Hartung HP, et al. Randomized trial of three IVIg doses for treating chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain. 2022;145(3):887-896. doi:10.1093/brain/awab422
INDICATIONS & IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR PANZYGA® IMMUNE GLOBULIN INTRAVENOUS (HUMAN) – IFAS 10% LIQUID PREPARATION
BOXED WARNING: THROMBOSIS, RENAL DYSFUNCTION, AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Please click here for Full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING.
- Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin intravenous (IVIg) products, including Panzyga. Risk factors may include: advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling central vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors.
- Renal dysfunction, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur in predisposed patients who receive IVIg products, including Panzyga. Patients predisposed to renal dysfunction include those with a degree of pre-existing renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, age greater than 65, volume depletion, sepsis, paraproteinemia, or patients receiving known nephrotoxic drugs. Renal dysfunction and acute renal failure occur more commonly in patients receiving IVIg products containing sucrose. Panzyga does not contain sucrose.
- For patients at risk of thrombosis, renal dysfunction, or acute renal failure, administer Panzyga at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
See Full Prescribing Information, Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)
Indications and Usage
Panzyga (Immune Globulin Intravenous [Human] – ifas) is indicated for the treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI) in patients 2 years of age and older; this includes, but is not limited to, congenital agammaglobulinemia, common variable immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and severe combined immunodeficiencies; chronic immune thrombocytopenia (cITP) in adults to raise platelet counts to control or prevent bleeding; and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in adults to improve neuromuscular disability and impairment.
Contraindications
Panzyga is contraindicated in patients who have a history of severe systemic hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, to human immunoglobulin and in IgA-deficient patients with antibodies against IgA and history of hypersensitivity.
Warnings and Precautions
- Monitor renal function, including blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine, and urine output in patients at risk of developing acute renal failure.
- Hyperproteinemia, increased serum osmolarity, and hyponatremia may occur in patients receiving Panzyga.
- Aseptic meningitis syndrome may occur in patients receiving Panzyga, especially with high doses or rapid infusion.
- Hemolysis that is either intravascular or due to enhanced red blood cell sequestration can develop subsequent to Panzyga treatments. Risk factors for hemolysis include high doses and non-O-blood group. Closely monitor patients for hemolysis and hemolytic anemia.
- Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions (transfusion-related acute lung injury [TRALI]).
- Monitor blood pressure prior to, during, and following Panzyga infusion.
- Carefully consider the relative risks and benefits before prescribing the high dose regimen (for cITP) in patients at increased risk of volume overload.
- Panzyga is made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents, e.g. viruses and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agent.
Adverse Reactions
- PI – The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of subjects were: headache, nausea, fever, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
- cITP in adults – The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of subjects were: headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and anemia.
- CIDP in adults – The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of subjects were: headache, fever, dermatitis, and blood pressure increase.
The risk information provided here is not comprehensive; See full Prescribing Information and Boxed Warning for Panzyga.
To report suspected adverse reactions, contact Octapharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-766-4860 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
INDICATIONS & IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR PANZYGA® IMMUNE GLOBULIN INTRAVENOUS (HUMAN) – IFAS 10% LIQUID PREPARATION
BOXED WARNING: THROMBOSIS, RENAL DYSFUNCTION, AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Please click here for Full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING.
- Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin intravenous (IVIg) products, including Panzyga. Risk factors may include: advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling central vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors.
- Renal dysfunction, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur in predisposed patients who receive IVIg products, including Panzyga. Patients predisposed to renal dysfunction include those with a degree of pre-existing renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, age greater than 65, volume depletion, sepsis, paraproteinemia, or patients receiving known nephrotoxic drugs. Renal dysfunction and acute renal failure occur more commonly in patients receiving IVIg products containing sucrose. Panzyga does not contain sucrose.
- For patients at risk of thrombosis, renal dysfunction, or acute renal failure, administer Panzyga at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
See Full Prescribing Information, Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)
Indications and Usage
Panzyga (Immune Globulin Intravenous [Human] – ifas) is indicated for the treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI) in patients 2 years of age and older; this includes, but is not limited to, congenital agammaglobulinemia, common variable immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and severe combined immunodeficiencies; chronic immune thrombocytopenia (cITP) in adults to raise platelet counts to control or prevent bleeding; and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in adults to improve neuromuscular disability and impairment.
Contraindications
Panzyga is contraindicated in patients who have a history of severe systemic hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, to human immunoglobulin and in IgA-deficient patients with antibodies against IgA and history of hypersensitivity.
Warnings and Precautions
- Monitor renal function, including blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine, and urine output in patients at risk of developing acute renal failure.
- Hyperproteinemia, increased serum osmolarity, and hyponatremia may occur in patients receiving Panzyga.
- Aseptic meningitis syndrome may occur in patients receiving Panzyga, especially with high doses or rapid infusion.
- Hemolysis that is either intravascular or due to enhanced red blood cell sequestration can develop subsequent to Panzyga treatments. Risk factors for hemolysis include high doses and non-O-blood group. Closely monitor patients for hemolysis and hemolytic anemia.
- Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions (transfusion-related acute lung injury [TRALI]).
- Monitor blood pressure prior to, during, and following Panzyga infusion.
- Carefully consider the relative risks and benefits before prescribing the high dose regimen (for cITP) in patients at increased risk of volume overload.
- Panzyga is made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents, e.g. viruses and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agent.
Adverse Reactions
- PI – The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of subjects were: headache, nausea, fever, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
- cITP in adults – The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of subjects were: headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and anemia.
- CIDP in adults – The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of subjects were: headache, fever, dermatitis, and blood pressure increase.
The risk information provided here is not comprehensive; See full Prescribing Information and Boxed Warning for Panzyga.
To report suspected adverse reactions, contact Octapharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-766-4860 or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.